|
Posted by Wade
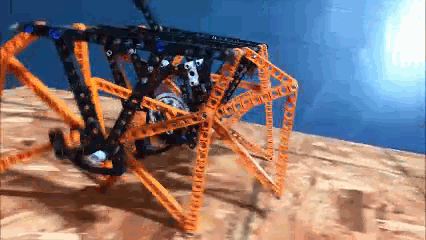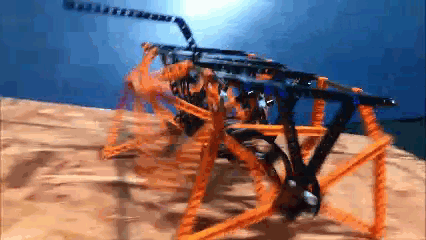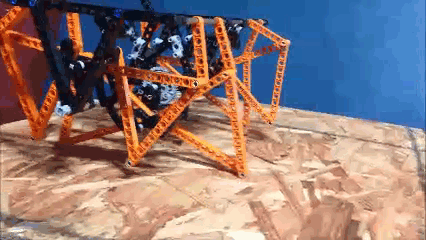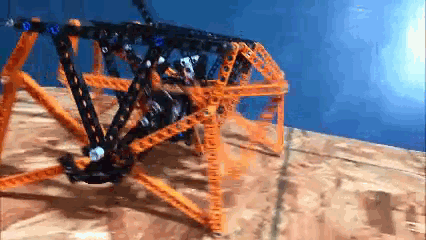
As we learned during our attempt to scale up TrotBot, not all robot's legs will walk by pushing or pulling the robot. When we pushed TrotBot Ver 0 with its more rectangular-shaped footpath, the cranks would initially rotate, and then the linkage would freeze and the feet would skid on the pavement. Instead, we had to manually rotate TrotBot's cranks to make it walk:
The same thing happened when we tried to push our LEGO Klann walkers with the motors disengaged - the feet would skid and the cranks would not rotate. In both cases, this was due to the linkage being at a sort of reverse Dead-Point.
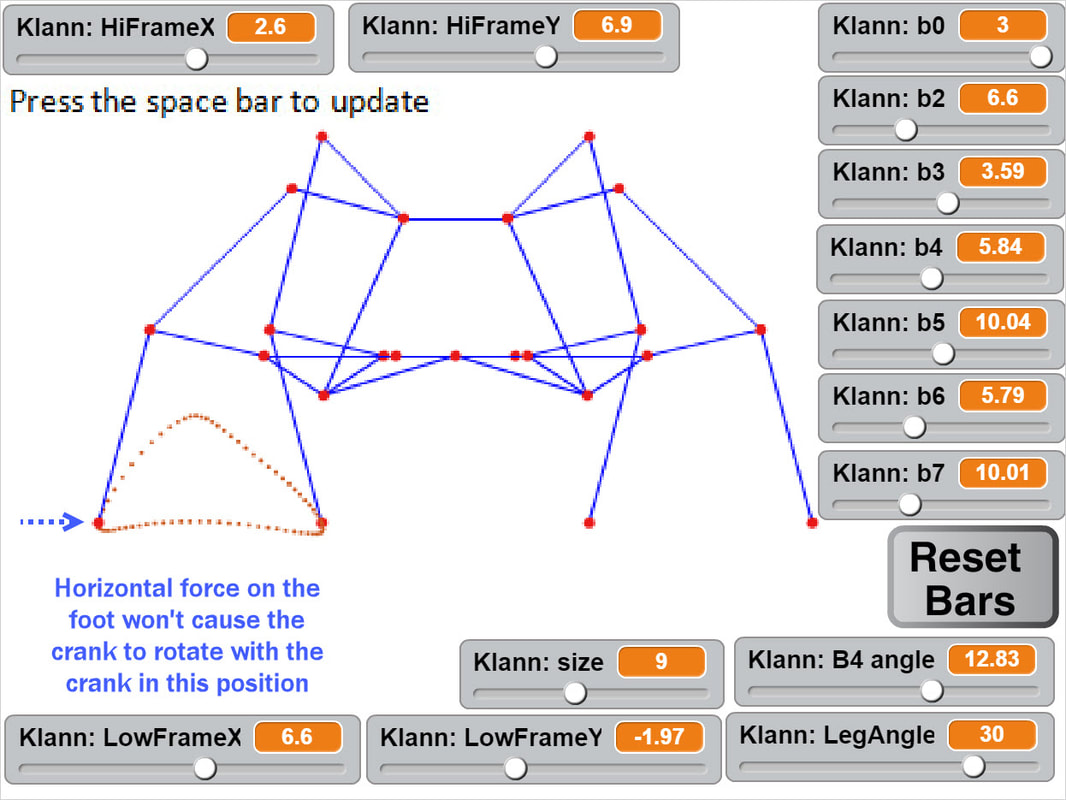
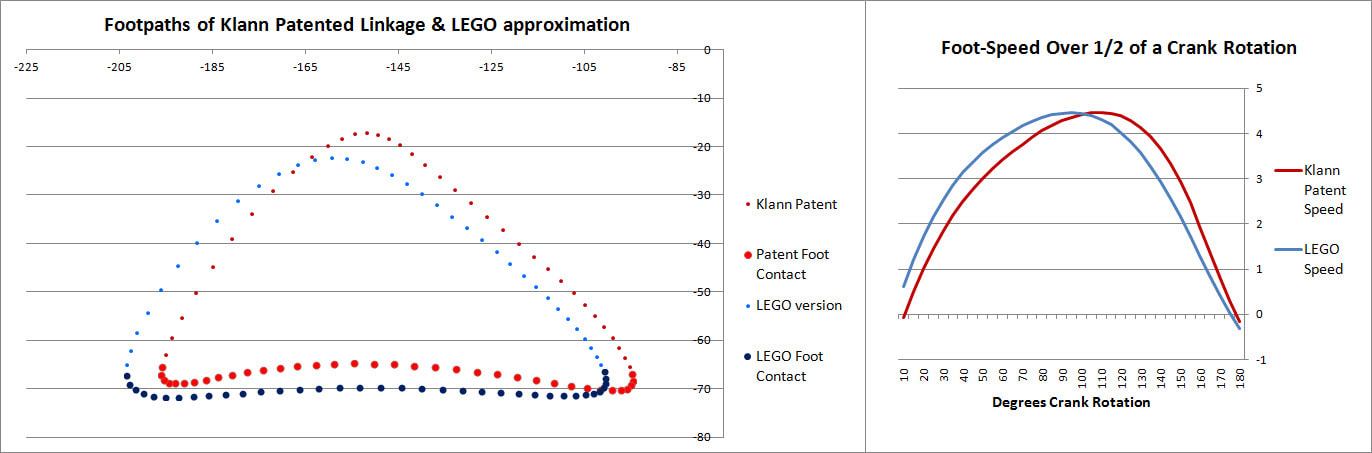
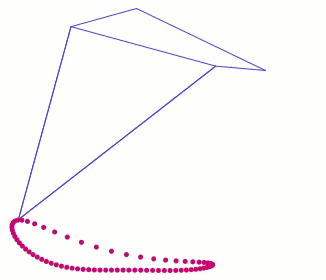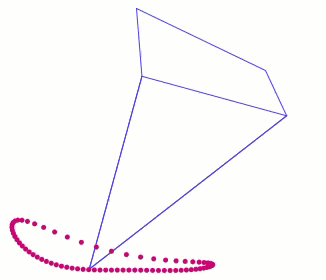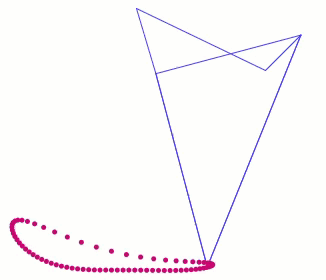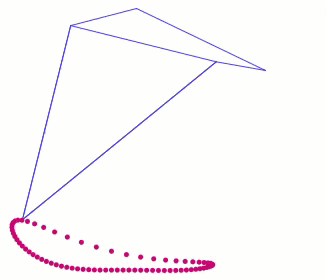
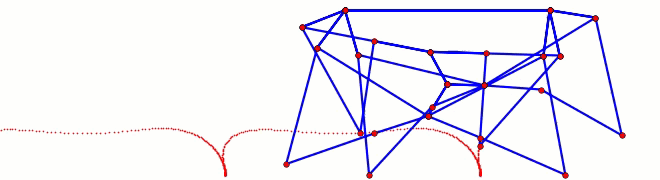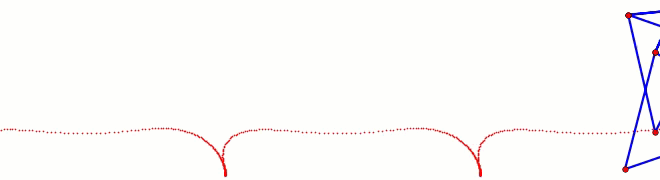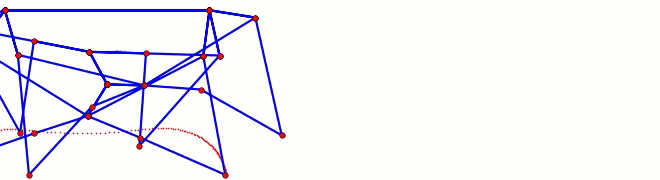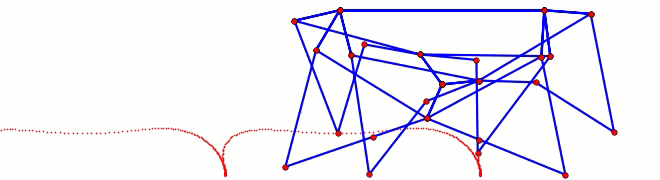
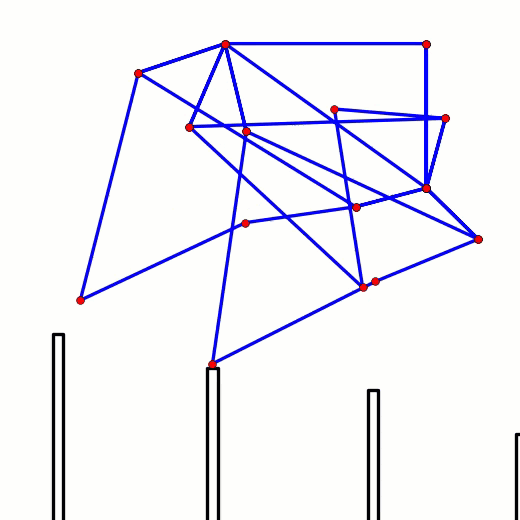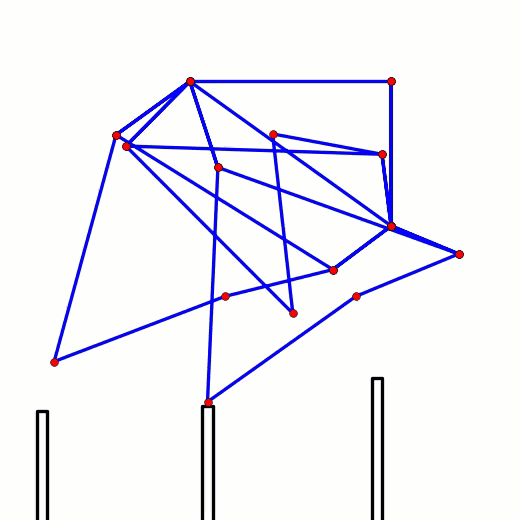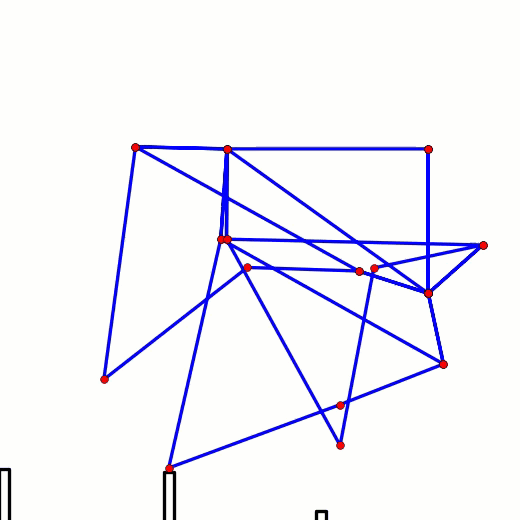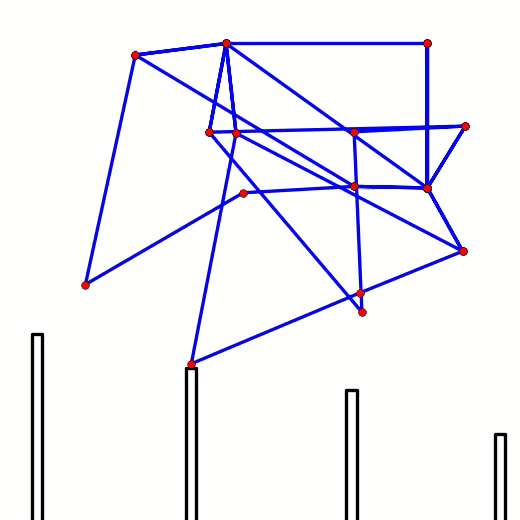
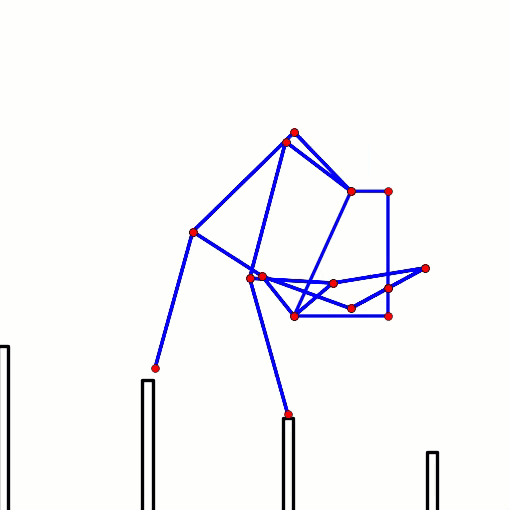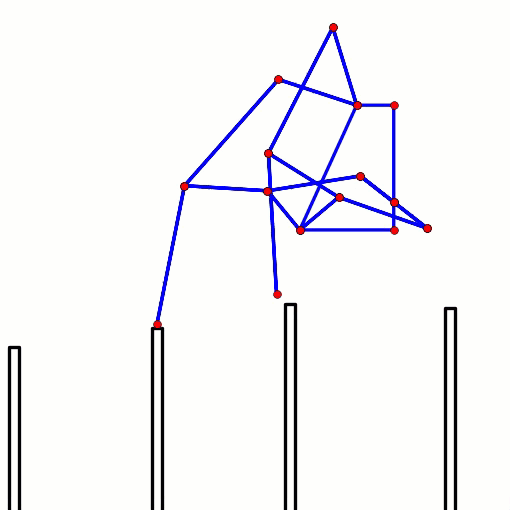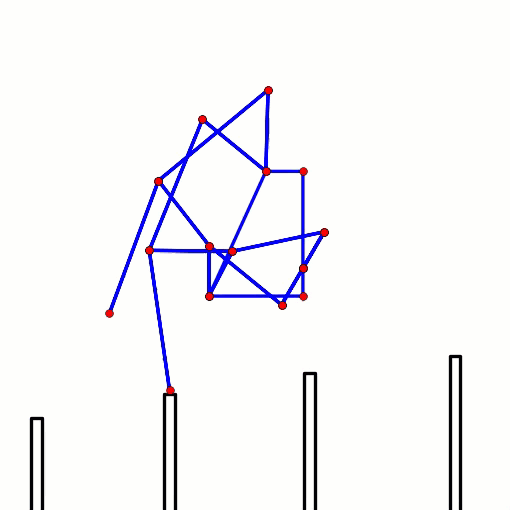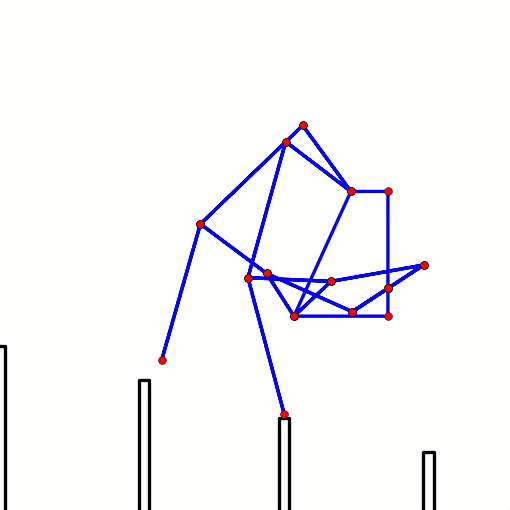
This behavior can be predicted from the image of Klann's linkage below. Notice that when the crank is in such a horizontal position, all four feet are at the bottom corners of Klann's triangular foot-path. Also notice that the feet slow to a virtual stop at these corners, as indicated by how bunched together the red dots are at the bottom corners of the foot-path. In other words, rotating the crank +/- 10 degrees from this horizontal position would barely cause the feet to move. This also means that pushing the robot (and hence the feet) would not cause the feet to move nor the crank to rotate. Instead, it would only cause the legs to bend and the feet to skid, as happens with our prototypes.
This behavior is also indicated by linked bars being parallel - notice in the image above that the legs' connections to the crank are parallel with the crank, a tell-tale sign of a Dead-Point.
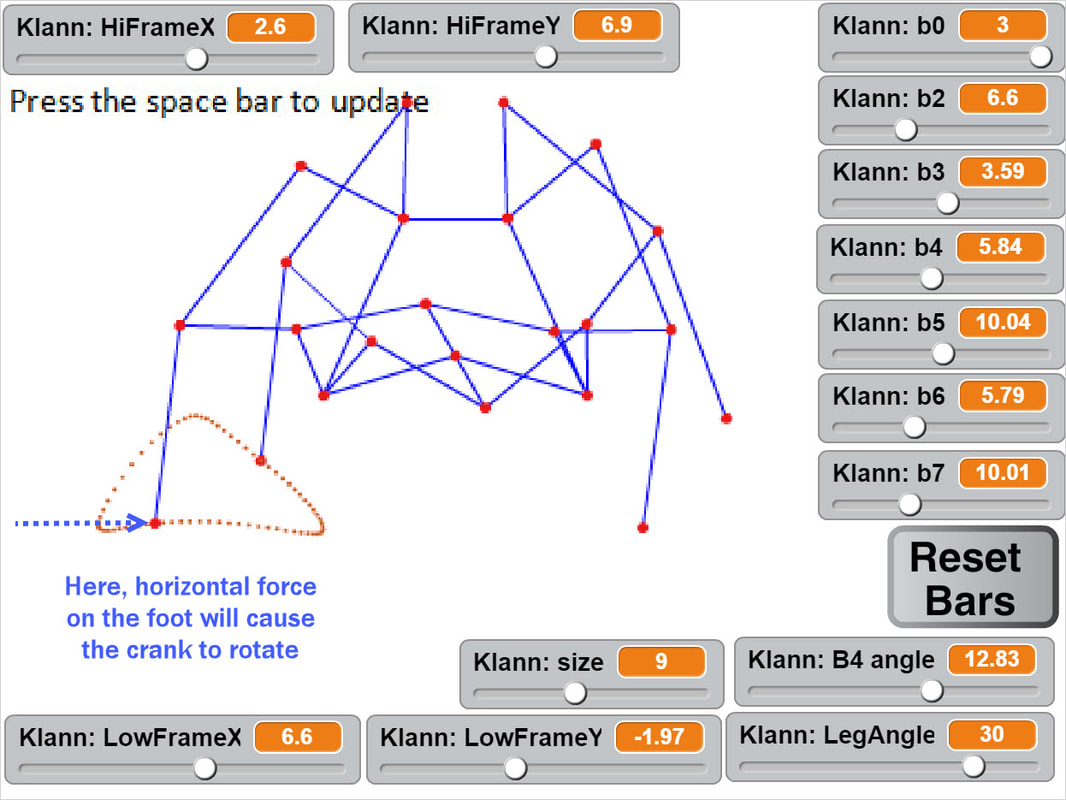
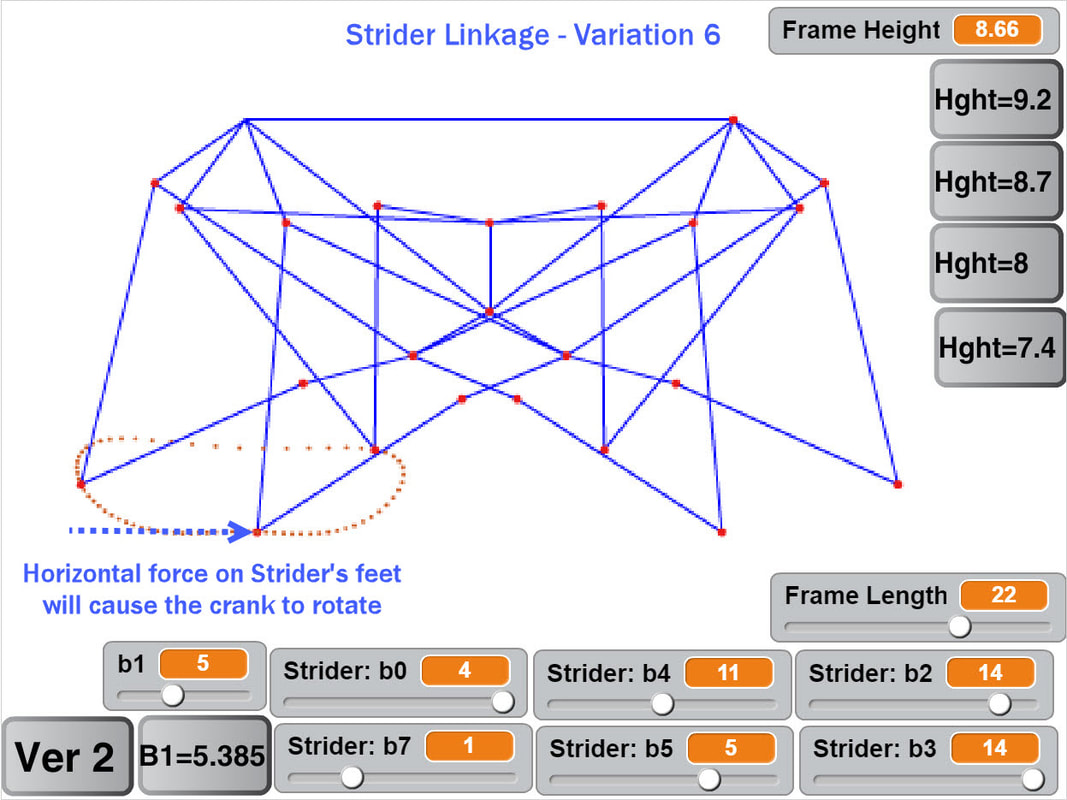
Below the crank has been rotated past this dead point where crank rotation causes foot movement and vice versa: If another pair of legs were added to each side of Klann, as done in the simulation of Strider below, then maybe its legs could be driven by pushing the robot (although one of Klann's feet would still skid at the corner of the foot-path, so it may not work so well - maybe adding feet that could slide or rotate a little would help?) Here's a test to see how easily this linkage variation #6 of Strider's mechanism can be driven by an external force - gravity in this case:
Notice how the robot wavers slightly to the left and right as it descends, due to the foot-speed varying a little. Linkage variation 7 below has more consistent foot speed, and waivers less
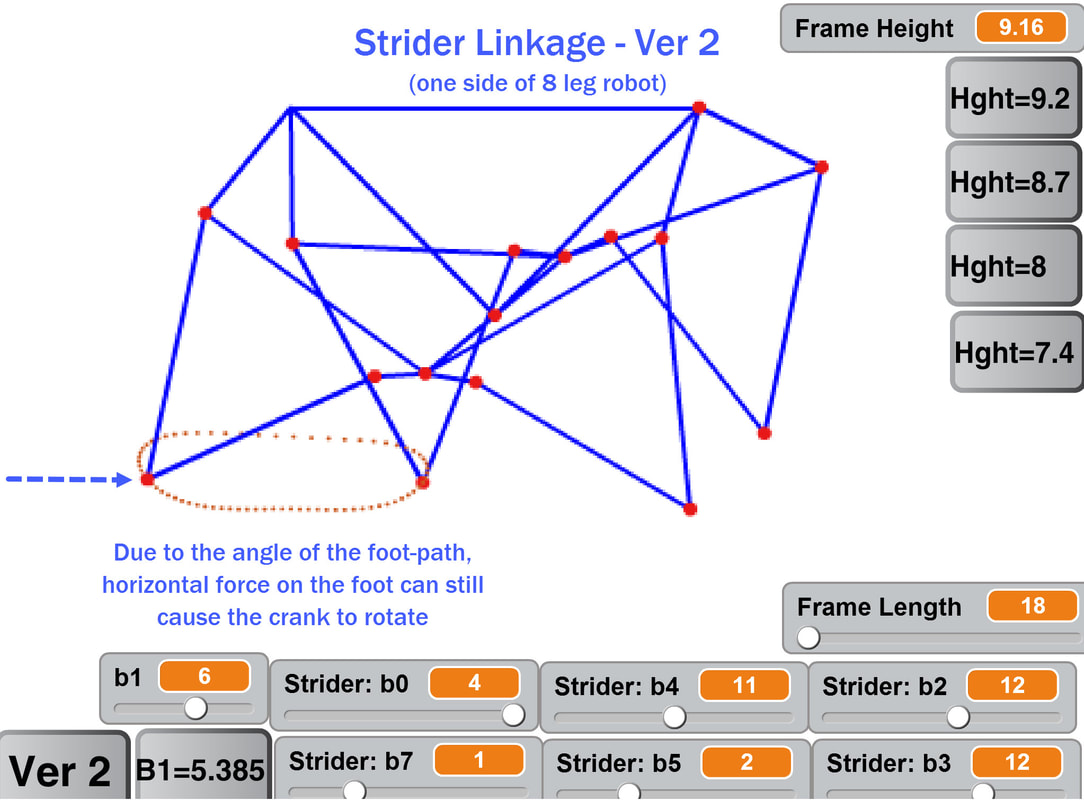
Passive walking can also be tested by pulling the robot with a rope: Strider's legs can also be driven by pushing the robot when built in an 8-leg version, although not nearly as efficiently as 12-leg versions, and the ramp's slope had to be increased to get an 8-legged Strider to walk below:
0 Comments
Posted by Wade
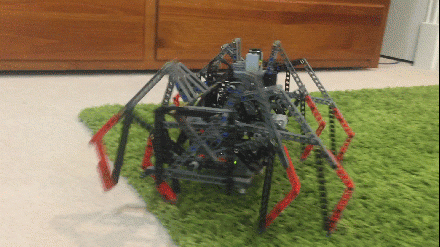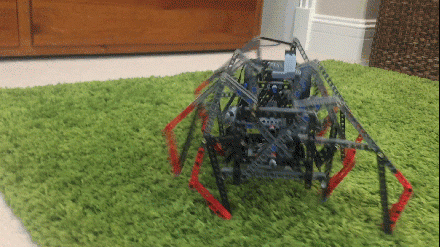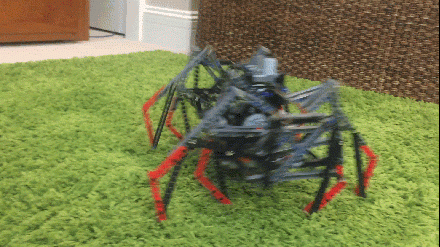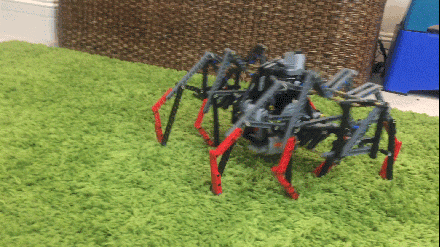
Like how we appreciate Nike's when running on concrete, large-scale walkers benefit from shock-absorbing feet. By increasing the spring's travel, shock-absorbing feet may also be able to smooth the gaits of high-stepping walkers like TrotBot and Strider. And of course this would create new problems to be solved! First, here's the Mondo Spider's feet in action, which provide some shock absorption, and they also slide on the smooth concrete, which helps with turning and with smoothing Klann's speed:
It walks amazingly fluidly considering how Klann's foot-path comes to a stop at each end, and the springs probably smooth the transition between feet somewhat:
Watching the video raises some questions, like:
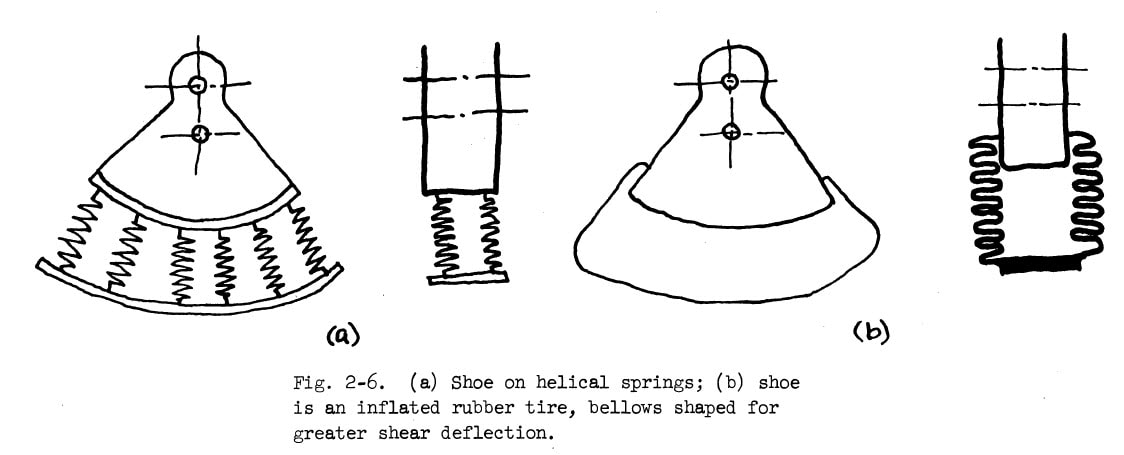
Implementing Klann's linkage without shock-absorbing feet that slide results in a more halting gait, as can be seen in this version of the Walking Beast: Our LEGO Klann walkers could also benefit from shock-absorbing feet when walking on hard surfaces like wood floors: Next, here are some shock-absorbing feet ideas from Mechanical Walker pioneer, Professor Joseph Shigley: Feet with such springs extend the feet toward the ground. So, in addition to absorbing shocks, the springs also increase the percentage of ground contact of each leg per crank rotation. Taken to an extreme, feet with very long springs could theoretically increase an 8-legged Strider's ground-contact to the point that it always had one foot on the ground at each corner of robot, and do so without causing the robot's height to drop when the feet touching the ground switch. This is because both of the feet will be near the ground at the foot transition, meaning two springs will be pushing the robot up, reducing how far the robot falls at foot transitions. However, a few of the (probably numerous) issues of long-spring feet are:
So, springs long enough to convert a large-scale Strider to an 8-legged walker wouldn't be feasible, but shock-absorbing feet can still help to reduce the force of impacts of feet with the ground. To illustrate, below are simulations of adding shock-absorbing feet to 12-leg versions of TrotBot and Strider (assuming perfectly elastic springs without damping that comply with Hook's Law, and ignoring inertia and spring oscillation): Notice how adding springs to TrotBot's feet causes the rear feet to skid slightly as its feet are lifted off the ground (because its foot-speed slows at that point in its foot-path). Strider's linkage simulated below has more consistent foot-speed, so its rear feet do not skid when springs are added As an alternative to springs, foam padding can be added to the feet which also provide some damping. This idea is tested below which explores how much an 8-legged Strider's gait can be smoothed by adding thick foam pads to its feet: Below tests foam "boots" on snow and ice: And thinner, foam weather stripping for doors was used in this feasibility test of a jumping robot: On a related note, our LEGO walkers' gaits are somewhat smoothed by the flexing of the metal support rods, although such shock-absorption isn't consistent since it varies depending on how far the legs are from the inner frame. You can see this in action in the following video, where the outer frames bounce more than the center frame: Walking Tanks? Applying Prof. Shigley's Pioneering Study of Mechanical Walkers to Strider's Linkage7/7/2018
Posted by Wade
If you are looking for ideas on how to create highly functional mechanical walkers, Professor Joseph Shigley's 1960 feasibility study for the army is a great resource. It combines engineering rigor and sound reasoning to illuminate many of the challenges, and potential capabilities of mechanical walkers.
To meet the requirements of walking tanks, Shigley sought a mechanism that could:
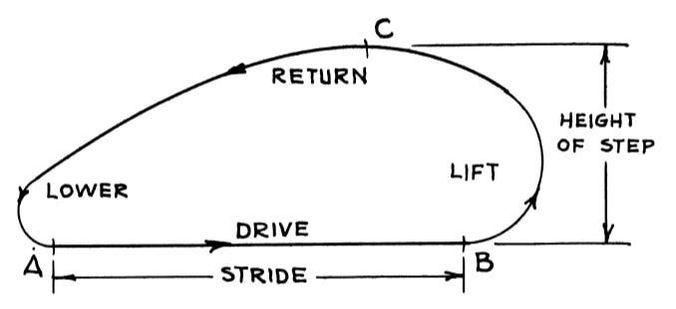
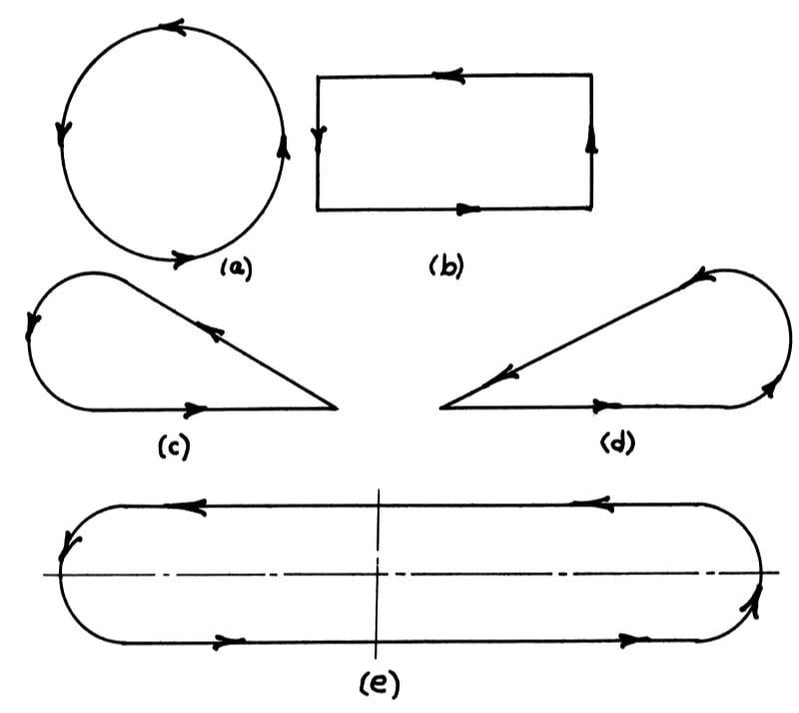
To meet the rugged terrain and speed requirements of tanks, much of Shigley's study focused on the foot-paths of mechanisms. Below is Shigley's diagram of foot-path types, with type E representing his ideal type for rugged terrain and fast speeds.
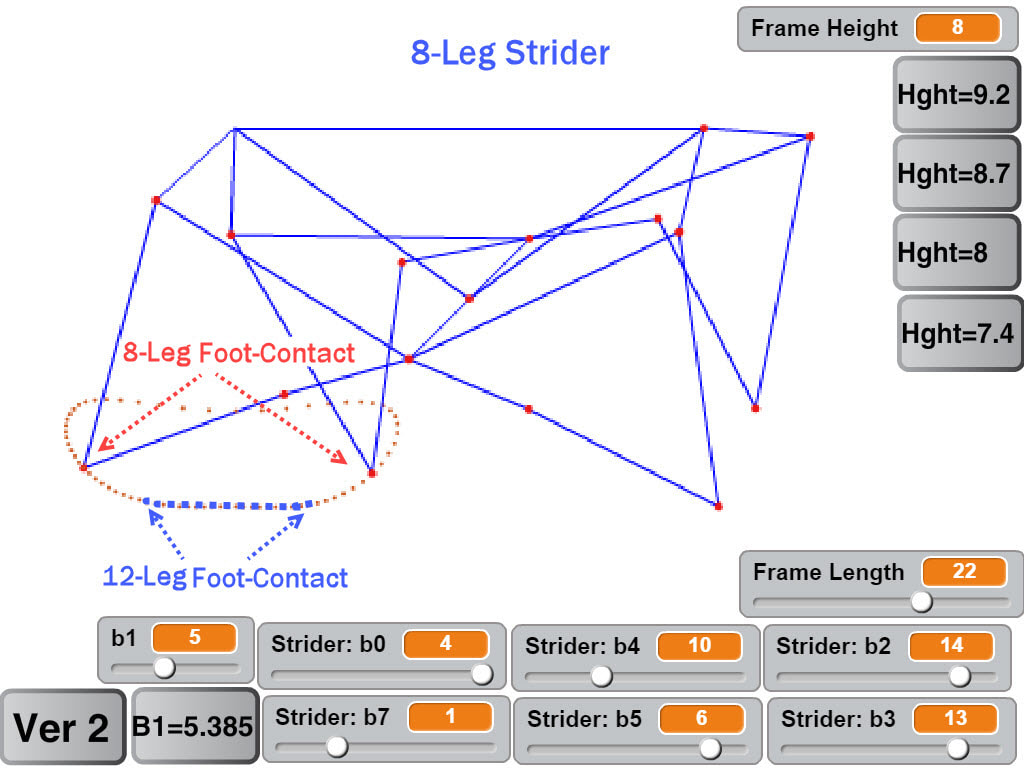
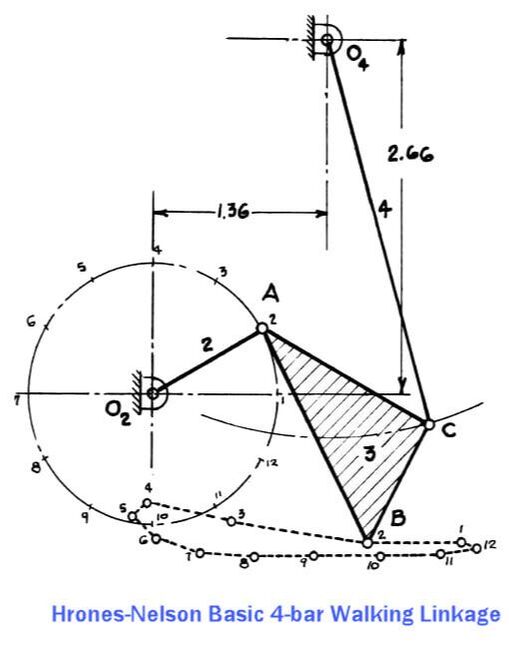
When Creating New Mechanisms, Start By Investigating 4-Bar Linkages In general, the fewer bars in a linkage, the better (lower costs and build-times, less mechanical complication and friction, etc.). So, searching for a mechanical solution based on a 4-bar linkage is usually a wise first step. Shigley advised searching thru Hrones-Nelson's atlas of hundreds of 4-bar linkage coupler curves as a "good first approach to such a problem", which must have been a vital resource for mechanical engineers in the days before personal computers. Below is one of the better 4-bar linkage configurations Professor Shigley found in Hrones-Nelson's atlas, but it doesn't step high enough for rugged terrain. Shigley described how the step-height could be increased by allowing a joint to slide along a cam groove, but we wanted a mechanism that could be prototyped in LEGO. So, instead we experimented with pairing two 4-bar linkages into a combined 10-bar linkage with front and back legs, such that the rear leg lifted the front foot and vice versa. This allowed us to increase the step-height significantly.
We found that the boat-shape of Strider's foot-path mitigates this problem, since the foot's horizontal speed during the lift and lower phases is similar to the foot-speed of the drive phase. This can be seen in the above GIF of Strider walking across the screen. Notice how the bottom halves of its lift and lower phases are nearly vertical, which means that when a foot steps on an obstacle halfway down its lower phase it will be less likely to skid or cause the robot's forward motion to stop while stepping up onto the obstacle.
The impact of the boat-shape can be exaggerated by reducing the number of legs from 12 to 8, causing the feet to contact the ground well above the bottom drive phase of a 12 leg Strider: You can see this in action in the below video of an 8-legged Strider walking on rocky terrain, where Strider's feet often contact the rocks well above the bottom drive phase, yet the robot's speed remains fairly consistent as it walks across the rocks: Triangular Foot-Paths How robot speed varies as ground height changes can also be gauged by simulating the front legs while keeping the mechanism horizontal, which results in fairly consistent speed for mechanisms with rounded foot-paths like Striders, and also serves to cushion the impact of hitting obstacles somewhat like a spring-based suspension: In contrast, the feet of robots with triangular foot-paths will be going the wrong way when stepping on/off obstacles, or when the terrain's slope changes abruptly. If the feet can't skid, then the change in the terrain's elevation can push the robot backward, as happens to Klann's Mechanical Spider below. If the rear legs aren't stepping on a similar obstacle at the same moment, then they'll be pushing the robot forward as usual, fighting the front legs and potentially jamming the mechanism. Here's a test of how Strider and Klann linkage robots handle elevation changes, using a slope change to make the test scale-independent: Foot-Path Symmetry The front-to-back symmetry of Strider's foot-path results in fairly consistent horizontal speed when the terrain's elevation changes on either side of its foot-path - e.g. when either ascending or descending the stilts in these simulations. In contrast, TrotBot's foot-path is somewhat teardrop-shaped. This causes TrotBot's horizontal speed to drop when encountering large elevation changes on the shorter, inner side of its foot-path, which can be seen in the below simulation when TrotBot steps down to a lower stilt:. Tank-Scale Functionality on Rugged Terrain? Strider's high-stepping, boat-shaped foot-path allows it to meet Shigley's rugged terrain requirements fairly well at LEGO-scale. However, tank-scale functionality on rugged terrain is another matter, which would require the robot to be strengthened dramatically due to the lower strength-to-weight-ratios of larger scales. Furthermore, increasing strength typically involves adding structure and motor power, which further increases weight, which requires even more structure, which adds even more weight and costs, etc.
The legs in particular would need to be strengthened, since walking along the side of a hill, or turning the walker tank-style while on rugged terrain would put a tremendous amount of sideways forces on the long legs - if it were even feasible at such large scales. However, adding too much structure and weight to fast-moving legs would create other problems. Instead, perhaps the lower half of the legs could be supported laterally by rails connected to the frame? Rails that created channels that the leg's path should follow? Positioned below the legs' knee and "hamstring" joints to reduce sideways forces on these weak points? Eh......for rugged terrain I think I'll stick to smaller-scale walkers, which also benefit from Shigley's insights.
High Speed Walking As Shigley described, an ideal walking mechanism for a tank should have the constant horizontal speed of a wheel, while also being able to step over obstacles that block wheels. Strider has relatively constant foot-speed, as indicated by how little the feet skid in the following video. Since the feet aren't constantly accelerating/de-accelerating the robot this improves the gait's efficiency, and Strider is the only mechanism that we've tested which can walk with a 1:1 gear ratio without the LEGO motors stalling: High Speed Vibration Shigley also described how the vertical and horizontal inertia forces of leg mechanisms should be balanced for a tank to walk fast without vibrating itself to death. Such vibration isn't much of a problem at LEGO-scales, but it gets exponentially worse as scale increases. If you've ever driven a vehicle where the steering wheel shakes due to its wheels being out of balance, and seen how it's corrected by attaching small metal weights to the wheels, then you can probably imagine how much worse the vibration problems could be for a vehicle with large mechanical legs running at high RPMs.
Strider's mechanism would need to be modified in order for a large-scale version to walk at high RPMs with limited vibration. If curious, Shigley's study below shows how to mathematically analyze inertia forces by calculating the horizontal and vertical accelerations of the legs' masses, and gives some suggestions for balancing them.
Load Bearing and the Linkage's Bar Count The more bars a linkage has, the more joints it needs. Each joint adds friction. Furthermore, the joints will always have some play, which can cause long legs with many joints to bend sideways under loads, especially when turning them tank-style. Like Klann's sturdy 6-bar linkage, Strider's linkage has relatively few bars per leg with 10 bars per leg pair, versus TrotBot's and Strandbeest's 8 bars per leg. If implemented well, this implies that Strider's linkage has the potential to be relatively energy efficient and should be able to handle loads relatively well. Below tests linkage variation #6 with a 25 pound load. The plastic parts bend and shift somewhat under the load, increasing the difficulty of carrying the load, but the LEGO motors didn't stall. Also, we were planning on uploading a video with Strider self-destructing at the end by attempting to turn it while carrying 25 pounds. Some of our other walkers self-destructed while carrying much less weight, so we were a bit surprised that Strider survived with its legs intact. Strider's low bar count per leg does appear to result in a stronger linkage.
Notice how adding the weight causes Strider v6 to have a stammering gait, which is partially due to Variation 6 having less consistent foot-speed than does Variation 7 featured in the slow motion video above.
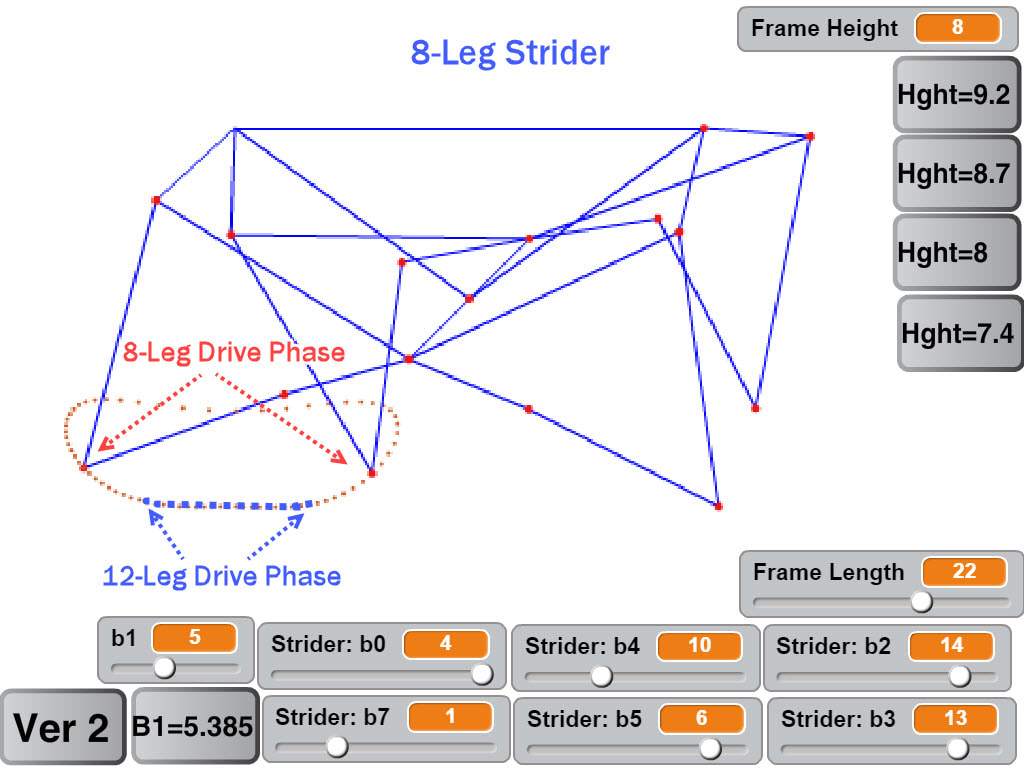
Before performing this test the plastic LEGO axles were replaced with steel axles to handle the torque. Other than that, and the 2 steel support rods, all of the parts are plastic LEGO parts connected by LEGO pins (no glue). Strider's linkage dimensions can be found here, and other configurations of Strider can be found here where you can also create your own customized Strider linkage with an interactive simulator. Below is Prof Shigley's feasibility study, a 1960 Popular Science article discussing it, and the Hrones Nelson Atlas of four bar linkage coupler curves.
|
Categories
All
Archives
February 2023
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed